
Products
Ball Mill Gearless Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Motor – High Starting Torque & Energy Saving
The PMDD motor is a high-efficiency drive system that directly couples a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) with the load, eliminating intermediate transmission components like gearboxes or pulleys.
Classification:
Working Principle of Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Motor
Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Motor (PMDD Motor) Working Principle
The PMDD motor is a high-efficiency drive system that directly couples a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) with the load, eliminating intermediate transmission components like gearboxes or pulleys. Its core operational principles are as follows:
Magnetic Field Generation
◇ Stator
Composed of three-phase windings that generate a rotating magnetic fieldwhen powered by variable-frequency AC.
◇ Rotor
Embedded with high-performance permanent magnets (e.g., NdFeB), creating a fixed magnetic field.
No external excitation or brushes/slip rings (brushless design).
◇ Synchronous Operation
Interaction between the stator's rotating field and rotor's permanent magnetic field forces the rotor to rotate at synchronous speed(Slip=0).
Speed is precisely adjusted (0–100% rated speed) via frequency control.
◇ Direct Load Coupling
The rotor shaft connects directly to loads (e.g., fan impellers, conveyor drums), bypassing gearboxes/couplings.
| Product | Product Category | Voltage | Power Range | Product Application |
| Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Motor (5-500rpm) | Explosion-proof | 380/415V/460V | 11KW-315KW,355KW-710KW | Oil & gas extraction (drilling rigs, oil pumps, compressors) Refineries (reactor agitators, centrifugal pumps) Chemical plants (flammable liquid transfer, gas compression) Underground ventilation fans, conveyor belt drives Coal dust transport equipment, drainage pumps Alcohol extraction workshops, spray drying towers Flour/sugar powder conveying systems, edible oil pressing equipment |
| 660V | 11KW-315KW,355KW-710KW | |||
| 1140V | 11KW-315KW,355KW-1600KW | |||
| 3300V/4610V | 200KW-1600KW | |||
| 6000V | 200KW-1600KW | |||
| 10000V | 200KW-1600KW | |||
| Non-explosion proof | 380/415V/460V | 11KW-315KW,355KW-710KW | For textile/engineering vehicles/belt machine tightening/air cooling island/flotation machine/separator/mixer/grinding machine/ball mill etc | |
| 660V | 11KW-315KW,355KW-710KW | |||
| 1140V | 11KW-315KW,355KW-3000KW | |||
| 3300V/4610V | 200KW-3000KW | |||
| 6000V | 200KW-3000KW | |||
| 10000V | 200KW-3000KW |
Advantages
◇ Transmission efficiency >98% (vs. 90–95% for geared systems).
◇ Eliminates gear wear/belt slippage.
◇ Torque Control
◇ Uses FOC (Field-Oriented Control) or DTC (Direct Torque Control) to regulate torque via current phase adjustment.
Core Advantages
◇ High Efficiency: IE4/IE5 energy class, 15–30% energy savings vs. traditional drives.
◇ Maintenance-Free: No gear oil/belts.
◇ Precision Control: Speed accuracy ±0.1%, fast dynamic response.
◇ Compact Design: 30–50% smaller than "motor+gearbox" systems.
Technical Specifications
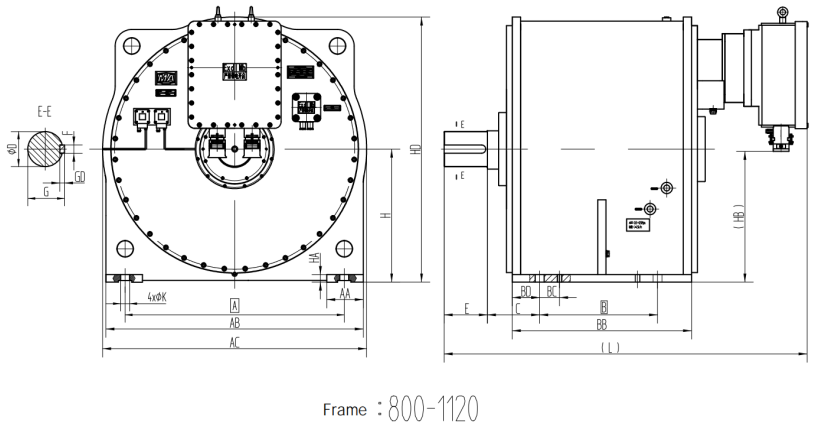
Voltage:380V/660V/1140V Other voltages customizable, up to 10kV
| Raled freguency (Hz) | Instalation size | Outline | ||||||||||||||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | K | AA | BB | BC | BD | GD | HA | HB | L | AB | AC | HD | |
| H450 | 670 | 560 | 280 | 110 | 150 | 28 | 100 | 450 | 42 | 150 | 840 | 80 | 140 | 16 | 35 | - | 1210 | 820 | 852 | 1340 |
| H560① | 900 | 560 | 315 | 150 | 180 | 36 | 138 | 560 | 42 | 180 | 970 | 120 | 180 | 20 | 35 | - | 1365 | 1080 | 1120 | 1575 |
| H560 | 900 | 800 | 315 | 180 | 220 | 45 | 155 | 560 | 42 | 180 | 1180 | 120 | 180 | 25 | 35 | - | 1620 | 1080 | 1120 | 1575 |
| H530 | 1000 | 800 | 335 | 210 | 240 | 50 | 193 | 630 | 54 | 200 | 1230 | 120 | 215 | 28 | 45 | - | 1720 | 1200 | 1250 | 1720 |
| H710 | 1120 | 900 | 315 | 230 | 260 | 50 | 213 | 710 | 54 | 200 | 1280 | 120 | 190 | 28 | 45 | - | 1750 | 1320 | 1140 | 1900 |
| HBDD | 1320 | 900 | 315 | 250 | 280 | 56 | 230 | 800 | 62 | 200 | 1280 | 120 | 190 | 32 | 45 | 880 | 2145 | 1520 | 1580 | 1595 |
| H900 | 1500 | 1000 | 315 | 270 | 300 | 63 | 250 | 900 | 62 | 20 | 1330 | 120 | 165 | 32 | 45 | 1010 | 2220 | 1700 | 1850 | 1825 |
| H1000 | 1700 | 1120 | 315 | 320 | 340 | 70 | 298 | 1000 | 62 | 220 | 1470 | 120 | 175 | 36 | 45 | 1220 | 2300 | 1900 | 2010 | 2025 |
| H1120 | 1900 | 1120 | 355 | 370 | 390 | 80 | 345 | 1120 | 62 | 220 | 1560 | 120 | 220 | 40 | 45 | 1500 | 2530 | 2120 | 2220 | 2230 |
| Rated torque (Nm) | Rated power (KW) | Frame | Model | Efficiency n% | Power factor cosφ | Rated current (A) | Maximum torque multiplier | Rated frequency (Hz) | |||
| Explosion-proof series | Non-explosion-proof series | ||||||||||
| 380V | 660V | 1140V | |||||||||
| 4711 | 37 | 450 | TBVF-37/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-37-40-450-(380or660or1140) | 92% | 0.97 | 63 | 36 | 21 | 20 | 25 |
| 5730 | 45 | TBVF-45/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-45-40-450-(380or660or1140) | 77 | 44 | 25 | |||||
| 7003 | 55 | TBVF-55/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-55-40-450-(380or660or1140) | 93 | 54 | 31 | |||||
| 9550 | 75 | 560 | TBVF-75/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-75-40-560-(380or660or1140) | 92.5% | 127 | 73 | 42 | |||
| 11460 | 90 | TBVF-90/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-90-40-560-(380or660or1140) | 152 | 88 | 51 | |||||
| 14007 | 110 | TBVF-110/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-110-40-560-(380or660or1140) | 186 | 107 | 62 | |||||
| 16808 | 132 | TBVF-132/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-132-40-560-(380or660or1140) | 222 | 128 | 74 | |||||
| 20373 | 160 | TBVF-160/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-160-40-560-(380or660or1140) | 269 | 155 | 90 | |||||
| 25467 | 200 | TBVF-200/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-200-40-560-(380or660or1140) | 337 | 194 | 112 | |||||
| 28013 | 220 | TBVF-220/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-220-40-560-(380or660or1140) | 373 | 215 | 124 | |||||
| 31833 | 250 | TBVF-250/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-250-40-560-(380or660or1140) | 423 | 244 | 141 | |||||
| 35653 | 280 | 710 | TBVF-280/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-280-40-710-(380or660or1140) | 93% | 0.96 | 476 | 274 | 159 | ||
| 40110 | 315 | TBVF-315/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-315-40-710-(380or660or1140) | ---- | 309 | 179 | |||||
| 45203 | 355 | TBVF-355/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-355-40-710-(380or660or1140) | ---- | 348 | 202 | |||||
| 50933 | 400 | TBVF-400/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-400-40-710-(380or660or1140) | 94% | ---- | 388 | 224 | ||||
| 57300 | 450 | TBVF-450/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-450-40-710-(380or660or1140) | ---- | 434 | 251 | |||||
| 63667 | 500 | TBVF-500/40YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-500-40-710-(380or660or1140) | ---- | 485 | 281 | |||||
| 71307 | 560 | 800 | TBVF-560/60YC (66/1140) | JXSDZ-560-60-800-(380or660or1140) | 94.5% | ---- | 540 | 313 | 37.5 | ||
| 80220 | 630 | TBVF-630/60YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-630-60-800-(380or660or1140) | ---- | 604 | 350 | |||||
| 90407 | 710 | TBVF-710/60YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-710-60-800-(380or660or1140) | ---- | 681 | 394 | |||||
| 101867 | 800 | 900 | TBVF-800/60YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-800-60-900-(380or660or1140) | 95% | ---- | 767 | 444 | |||
| 114600 | 900 | TBVF-900/60YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-900-60-900-(380or660or1140) | ---- | 859 | 497 | |||||
| 127333 | 1000 | TBVF-1000/60YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-1000-60-900-(380or660or1140) | ---- | 954 | 552 | |||||
| 142613 | 1120 | 1000 | TBVF-1120/80YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-1120-80-1000-(380or660or1140) | 95.5% | ---- | 1069 | 619 | 50 | ||
| 159167 | 1250 | TBVF-1250/80YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-1250-80-1000-(380or660or1140) | ---- | 1193 | 691 | |||||
| 178267 | 1400 | TBVF-1400/80YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-1400-80-1000-(380or660or1140) | ---- | 1336 | 773 | |||||
| 203733 | 1600 | 1120 | TBVF-1600/80YC (660/1140) | JXSDZ-1600-80-1120-(380or660or1140) | 95.5% | 1527 | 885 | ||||
Jasung's Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Motors Revolutionize Ball Mill Systems
Jasung's permanent magnet direct drive (PMDD) motors have been widely adopted in ball mill systems, replacing traditional induction motor drives due to their unparalleled advantages:
1.Simplified Transmission
◇ Eliminates gearboxes, reducing mechanical complexity and potential failure points.
2.Maintenance-Free Operation
◇ No lubrication or periodic part replacements required, significantly lowering lifecycle costs.
3.Ultra-High Energy Efficiency
◇ Achieves IE5 efficiency (>96%), delivering 15-30% energy savings compared to geared systems.
4.Low Noise & Vibration
◇ Operates below 75dB, creating a safer and more environmentally friendly workplace.
5.Superior Starting Performance
◇ High starting torque (200-300% rated torque) with low inrush current, ideal for heavy-duty ball mill startups.
6.Smooth Grid Integration
◇ Soft starting capability prevents power grid disturbances and mechanical shocks to connected equipment.
7.Exceptional Load Handling
◇ Rapid torque response and 250% overload capacity handle load fluctuations and impact loads effortlessly.
Typical Applications
| Fans/Pumps: Cooling towers, centrifugal fans (direct impeller drive). Conveyors: Belt conveyors, hoists (direct drum coupling). Heavy Machinery: Coal mills, ball mills (high-torque starts). |  |
FAQ
Q: What are the Permanent Magnet Direct Drive (PMDD) Motors vs. Induction Motors - Key Differences:
Answer:
◇ Efficiency
PMDD: >96% (IE5)
Induction: 90-95% (IE3/IE4)
◇ Control
PMDD: Precise speed (±0.1%)
Induction: Slip (2-5% speed drop)
◇ Maintenance
PMDD: No brushes/gearbox
Induction: Needs regular maintenance
◇ Starting
PMDD: High torque, low current
Induction: Needs starter
◇ Size
PMDD: 30-50% smaller
◇ Cost
PMDD: Higher initial cost
Q:Can permanent magnets demagnetize? How to prevent it?
Answer:Demagnetization risks: High temperature (>150°C), strong reverse magnetic fields, or mechanical impacts may cause demagnetization.
Preventive measures:
◇ Use high-temperature-resistant magnets (e.g., NdFeB N42SH, HcJ≥35kOe).
◇ Design motor with protective slots for magnets.
◇ Install temperature sensors for real-time monitoring.
Q: Does PMDD require a drive? Can it start directly from line power?
Answer:Drive required:
◇ PMDD needs a variable frequency drive (VFD) for speed control.
◇ Direct line power startup may cause loss of synchronization and current surges (potential motor damage).
Recommended control methods: Field-oriented control (FOC) or direct torque control (DTC).
Q:What are the protection ratings for industrial PMDDs? How to select?
Answer: Common protection ratings:
◇ IP65: Dustproof + water jet protection (suitable for general industrial environments).
◇ IP66/IP67: Dustproof + strong waterproofing (for harsh environments like chemical plants and mines).
◇ Explosion-proof: Ex d IIC T4 (for hazardous areas like oil & gas).
Q: PMDD Motor shutdown setting
Answer: Design 2 PT100 embedded temperature sensors, at least one sensor for each bearing, the motor shutdowns when stator coil temperature reach 120℃ and bearing temperature reach 85℃
Q: The technical specifications of the water cooling system
Answer: Water cooling interface: standard 1-inch K-type mining quick connector. Need to connect to Jasung water cooler.
it is not recommended to use on-site natural water as it can easily block the drum water channel. The inlet pressure of cooling water is 0.6 MPa, and the water flow rate is 3 cubic meters per minute (3 m³/min)
A Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Motor is an advanced electromechanical system that integrates high-energy permanent magnets directly into the rotor structure and eliminates all intermediate mechanical transmission components such as gearboxes, belts, or couplings. By transmitting torque directly from the motor to the load, this technology significantly enhances efficiency, reliability, and dynamic performance while reducing mechanical complexity, vibration, and long-term maintenance costs. The direct drive motor has become a core technology in modern high-performance applications that demand precision, high torque density, and exceptional operational stability.
Permanent magnet materials—typically neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB), samarium cobalt (SmCo), or specialized rare-earth magnet formulations—are strategically embedded in the rotor to generate a strong and stable magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the precisely controlled stator windings to create smooth electromagnetic torque without the energy losses associated with rotor current induction. As a result, direct drive motors offer exceptionally high energy conversion efficiency, often exceeding 90–95% depending on the system's design. Because there is no need for rotor copper winding, rotor slip rings, or cooling channels used in traditional induction motors, the rotor is mechanically simple, thermally stable, and extremely durable.
One of the defining advantages of a direct drive architecture is the elimination of gear reduction systems. Gearboxes introduce friction losses, lubrication requirements, heat generation, and mechanical wear. Over time, these issues increase operating costs and reduce system reliability. By removing the gearbox entirely, direct drive motors achieve near-silent operation, dramatic reductions in mechanical loss, and long service life. The direct connection also allows for precise speed control, instantaneous torque response, and higher positional accuracy. These capabilities are especially valuable in robotics, industrial automation, semiconductor equipment, aerospace mechanisms, and precision manufacturing systems where motion performance must be consistent and repeatable.
In wind power applications, permanent magnet direct drive motors—often functioning as direct drive generators—enable wind turbines to operate at lower rotational speeds while producing high torque output. This reduces drivetrain failures, eliminates lubrication systems associated with high-speed gearboxes, and improves overall turbine availability and efficiency. The high torque density of direct drive machines allows for compact nacelle designs, reduced structural loads, and improved integration with power electronics. As global renewable energy demand grows, direct drive generator technology continues to gain widespread adoption in both onshore and offshore wind energy installations.
In robotics and automation, direct drive motors provide superior dynamic response, enabling robots to execute rapid, precise, and repeatable movements. High-resolution encoders combined with direct drive architectures allow robotic arms, collaborative robots, and autonomous systems to achieve ultra-smooth motion profiles. Direct drive actuators are commonly used in semiconductor wafer handling systems, lithography stages, gantry platforms, medical robots, and other applications where sub-micron positioning accuracy is essential. The absence of gears reduces backlash to nearly zero, enabling consistent and predictable control accuracy even after long-term usage.
In industrial machinery, permanent magnet direct drive motors are utilized in compressors, extruders, textile machinery, printing systems, injection molding machines, and large-scale material handling equipment. Their high efficiency reduces energy consumption, while their strong torque capability enables machines to operate at variable speeds without sacrificing power. This is beneficial for industries seeking to implement energy-saving upgrades or to comply with increasingly strict efficiency regulations. Direct drive motors often pair with variable frequency drives or servo controllers, forming an intelligent and adaptive powertrain capable of optimizing performance under diverse operating loads.
In the transportation sector, direct drive technology is widely applied in electric vehicles, rail traction systems, marine propulsion, and aerospace actuators. The compactness, reduced weight, and high torque density of direct drive motors directly contribute to improved energy utilization and extended operating range. Electric vehicle manufacturers use direct drive motors to improve acceleration performance and driving efficiency because the direct drive structure provides smooth torque without the delays or losses typically associated with multi-stage gear transmissions. In marine environments, corrosion-resistant direct drive propulsion systems offer quiet operation and high maneuverability, contributing to reduced environmental impact and enhanced operational reliability.
Another important advantage of Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Motors is their low maintenance requirement. Without gears, lubricants, or mechanical contact surfaces, the number of failure points is drastically reduced. This results in longer service intervals, lower lifecycle costs, and enhanced uptime. Direct drive motors also exhibit low heat generation due to the efficient magnetic circuit and reduced electrical losses. Improved heat dissipation enhances motor longevity and allows for higher continuous torque output. Advanced cooling systems—air cooling, liquid cooling, or integrated thermal pathways—can be incorporated depending on application requirements.
From a design perspective, direct drive motors come in multiple configurations, including axial-flux, radial-flux, and transverse-flux geometries. Axial-flux direct drive motors, known for their pancake-like structure, offer high torque density and compact designs suitable for wheel motors, robotics joints, and compact industrial systems. Radial-flux designs resemble traditional motors but incorporate optimized magnet layouts to achieve high torque and efficiency. Transverse-flux direct drive motors, while more complex, deliver extremely high torque at low rotational speeds and are used in heavy-duty and specialized industrial applications. Each architecture can be customized with specific magnet arrangements—surface-mounted, buried interior magnets, or Halbach arrays—to achieve desired performance characteristics such as higher torque, reduced cogging, or improved flux concentration.
Control systems play a critical role in direct drive motor performance. Field-oriented control, direct torque control, and advanced sensorless algorithms ensure precise electromagnetic control, efficient torque delivery, and smooth low-speed operation. Direct drive motors commonly integrate high-resolution encoders or resolvers to support precise feedback. For extreme environments—such as offshore turbines, aerospace vehicles, or high-temperature industrial settings—robust insulation, protective coatings, and reinforced housings ensure long-term performance under demanding conditions.
Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Motors support sustainable engineering goals due to their high energy efficiency and reduced mechanical waste. Although rare-earth magnets require careful sourcing and higher initial cost, ongoing advancements in magnet technology, motor design, and recycling processes continue to reduce cost barriers and increase accessibility. Innovations such as ferrite-based direct drive motors and reduced-rare-earth hybrid magnet formulations help further expand market adoption.
Overall, this technology represents a major evolution in modern motion systems, offering unmatched torque density, high efficiency, precise control, and long-term durability. Across renewable energy, robotics, electric vehicles, manufacturing equipment, and aerospace technologies, Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Motors contribute to higher performance, greater energy savings, and lower environmental impact. As industries continue to pursue smarter, more efficient, and more reliable solutions, direct drive motors will remain a cornerstone of next-generation electromechanical design, driving innovation and supporting the transition toward cleaner and more intelligent power systems.
Keyword:
Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Motor
Stator
Rotor
Direct Load Coupling
best Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Motor
Previous Page
Previous Page
Find Your Products
Keywords:Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Pulley | Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor | Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Motor
Related Products
Online Message
Please leave your email, our professional person will contact you asap!